

recoveries



Focused











"No matter what we do to deter waste and fraud, whistleblowers are the key to the government finding out about it when it happens."
Young Law Group specializes in representing whistleblowers. Our personalized, hands-on approach to representing whistleblowers starts with the fact that firm founder, Eric L. Young, is actively involved in each case. This level of personal attention and involvement differentiates YLG from other firms. We are selective and only accept a limited number of cases. This allows us to focus our attention on the details of every case and provide exceptional, quality representation in the process. Becoming a whistleblower can be an incredibly difficult and challenging decision. Exceptional lawyers who understand the process can help lighten your burden.
At YLG, we continue to strive to be the best. At the outset of any potential case, YLG lawyers will consult with the prospective whistleblower to learn about the facts and circumstances compelling them to act. From there, we develop the best strategy for not only protecting the whistleblower, but also for successful resolution of the case. YLG’s proven process is not limited to acting on the information provided by a client. In order to present the most compelling possible case to federal and state agents, we regularly engage our own forensic accountants and investigators to ensure that all relevant evidence is collected for the benefit of our client’s case. Our proven track record of success speaks for itself.
Meet Our Firm Founder
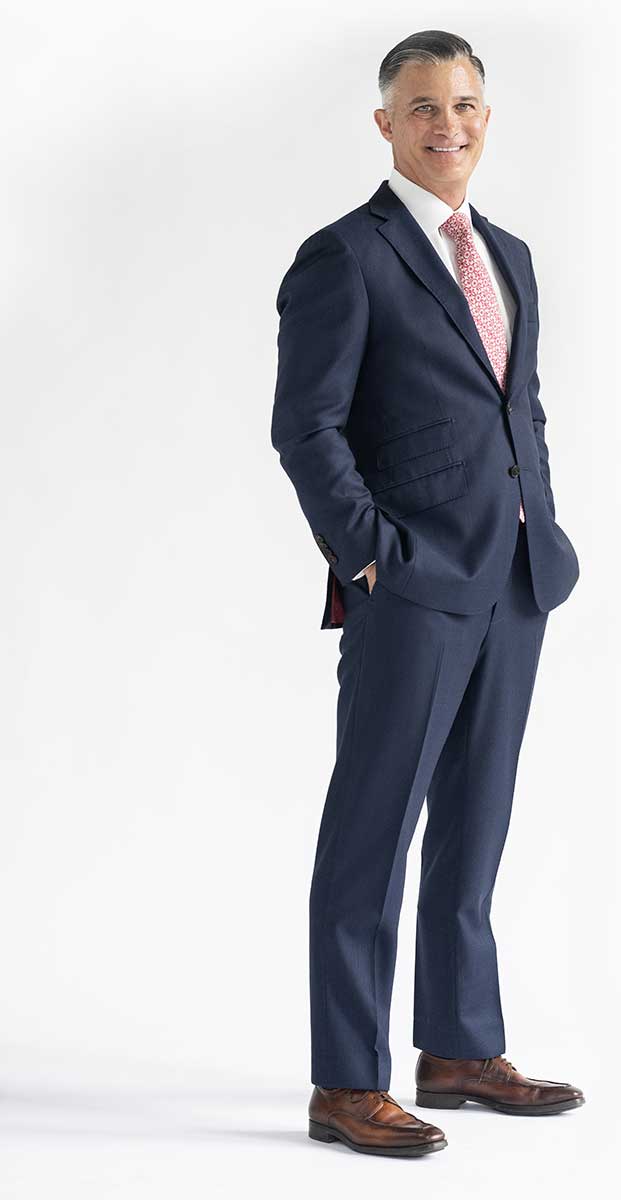

Young Law Group’s founder Eric L. Young is a seasoned member of the plaintiff’s bar with a distinguished track record in whistleblower litigation. Eric is AV-Rated by Martindale-Hubbell – the highest distinction for legal experience and ethics. In addition to securing the first-ever mandatory tax fraud whistleblower award, Eric has represented whistleblowers in several of the nation’s largest qui tam recoveries under federal and state false claims acts.
Eric has represented whistleblowers ranging from blue-collar workers to C-suite executives in the United States as well as Great Britain, China, Hong Kong, India, and South Africa.
The preeminent organization promoting whistleblowers’ rights, Taxpayers Against Fraud Education Fund, honored Eric as one of two Lawyers of the Year (2020) for achieving justice for three clients in two separate whistleblower cases against mega-pharmaceutical manufacturers, Novartis and Teva, resulting in settlements exceeding $800 million.
Eric’s record of accomplishments has distinguished him as one of the nation’s leading whistleblower attorneys. As Young Law Group’s managing partner, his primary focus is counseling clients who contemplate reporting corporate fraud to the government. He regularly represents relators in qui tam actions filed under the False Claims Act, as well as clients providing information under the whistleblower programs of the Securities and Exchange Commission, the Commodity Futures Trading Commission, and the Internal Revenue Service.
Eric L. Young
Firm Founder
PRACTICE AREAS
Our firm’s primary focus, the False Claims Act provides legal safeguards and benefits to encourage people to expose illegal or unethical actions.
We have already helped recover over $3,000,000 for the US government.
Class actions are a type of lawsuit where a group of people collectively sue a defendant for similar claims.
Class actions can be more efficient and cost-effective than individual lawsuits, as they allow for one trial to resolve multiple claims.
The legal rights and obligations of employers and employees in the workplace.
It covers a wide range of issues, including regulations related to unions, collective bargaining, workplace safety, discrimination, harassment, wages, and benefits.
Since its 2011 inception, the SEC Whistleblower Program has led to over $5.4 billion in sanctions against wrongdoers, with more than $1.3 billion returned to investors. To date, whistleblowers have been awarded around $1.3 billion.
"I recently had the pleasure of working with Young Law Group and could not be more satisfied with the results. They were incredibly professional and thorough in their work and always put my best interests first. I was able to trust them completely and had complete faith in their ability to get me the best outcome. I highly recommend Young Law Group to anyone looking for a top-notch law firm!"

C. A.
Whistleblower Client
"My experience with Eric Young and his law firm was outstanding. They were sensitive to my issues and were creative in helping to present the best case possible to the Department of Justice. Eric worked tirelessly in bringing my case to a successful outcome. Young Law Group attorneys were knowledgeable and experienced and provided me with sound legal advice throughout the process. They were always available to answer our questions and provide me with guidance. I am very pleased with the results and would highly recommend them to anyone considering a whistleblower action."

H.S.
Whistleblower Client
"I am very grateful for Young Law Group’s representation. They were extremely knowledgeable and professional throughout the process. They answered all of my questions and provided me with sound legal advice. The outcome of my case was much better than I expected, and I would highly recommend their services to anyone considering a whistleblower action."

J.S.
Whistleblower Client
"My experience with Young Law Group has been nothing short of outstanding. From the first contact with the firm, I felt taken care of and well represented. Their attention to detail and prompt responses to my questions and concerns was greatly appreciated. They were extremely knowledgeable about whistleblower laws and helped to ensure a successful outcome for my case. I highly recommend Young Law Group for all your legal needs. Thank you for all your hard work!"

J.O.
Whistleblower Client
"Eric Young and his law firm provided me with invaluable advice and kept me informed throughout the entire process I went through in deciding to file a whistleblower case. They were always available to answer any questions I had and made sure I was aware of all my rights and responsibilities. I would definitely recommend Young Law Group to anyone considering filing a whistleblower claim."

T.M.
Whistleblower Client
I have had the pleasure of working with Eric Young, Esquire for several years. He is an excellent attorney who is knowledgeable and professional. He is a great listener and has an ability to quickly assess a situation and develop an effective strategy. He is also a great negotiator and has an excellent understanding of the law. He has a great sense of humor and is always willing to go the extra mile to ensure the best outcome for his clients. Eric is truly an asset to any legal team and I highly recommend him.

R.R.
Class Action Client

